As with Randstad and Manpower, Robert Half revenue and earnings continue to decline. Decreases in full time placement, particularly with IT, are key drivers. According to the latest labor reports, the US labor market is seeing decreases in hiring and decreases in quits. People are staying at their jobs.
This trend is juxtaposed with a huge boom in Generative AI infrastructure. The initial boom is Gen AI capital investment into chips, data centers, and power generation. Gen AI applications and use cases are taking off are in software development, sales, customer service, and marketing.
The narrative VCs are pushing is that Gen AI will be bigger than the cloud and that Gen AI is “services sold as software” (a play on the software-as-a-service). Startups and mid market companies are announcing “caps” on how many people they will hire — ever. Avoiding an attempt at macro economics, I do want to look at some of the anecdata.
Robert Half Earnings
Performance
Revenue: Declined to $1.476 billion, down 14% year-over-year.
Revenue Breakdown: U.S. talent solutions revenues were $764 million, down 19% year-over-year. Non-U.S. revenues were $248 million, down 10%.
Client and Candidate Caution: Continues to impact hiring decisions and project initiations.
Economic Sensitivity: Certain segments like tech consulting still face challenges due to budget constraints.
Recovery Shape: Management expects a "spring-loaded" rebound in hiring, supported by high job opening levels. (Author note: we’ll come back to the job openings level)
Robert Half Earnings Commentary
Robert Half’s revenue decline closely matches what is happening in the (US) economy. People are hiring less, particularly in key segments for Robert Half. As they hire less, they use fewer contract solutions, too.
Robert Half’s business lines are contract solutions (staffing), permanent solutions (placing people in role), and Protiviti (their consulting solution).
The biggest segment line of business is contract solutions for Finance and Accounting (which RHI 0.00%↑ is known for).
Contract Finance and Accounting was down 17% year-on-year, but it accounted for slightly over half of Robert Half’s Decline.
Technology contract solutions were down almost 20%, but it’s a much smaller revenue segment.
Indeed.com’s Hiring Lab team provides a look at job postings trends, by country and sector. Looking at Finance, Tech, and Customer Service (the other big revenue category for Robert Half), the trends in job postings closely match what Robert Half is seeing in revenue changes.
By itself, we see a macro picture affecting RHI and other staffing companies. The juxtaposition with Gen AI cloud providers like Microsoft, Google, and Amazon is interesting, though.
Gen AI Cloud Providers Through the Labor Market Lens
Gen AI hyperscalers reported excellent results:
Alphabet quarterly revenues of $80.5B, up 15% year-on-year (YoY). Cloud, which sells AI servers, was up 28%.
Amazon revenues of $143.3B, up 13% YoY. AWS, was up 17.2% year-on-year.
Microsoft revenues of $61.9B, 17% YoY. Azure (cloud) up 31%, with a 7 point contribution from AI services.
Demand for Gen AI and AI services are surging among cloud providers.
In the latest set of earnings call, Satya Nadella, the CEO of Microsoft opined about what Generative AI will mean for the future-of-work.
Now on to future of work, we are seeing AI democratize expertise across the workforce. What inventory turns are to efficiency of supply chains, knowledge turns, the creation and diffusion and knowledge are to productivity of an organization. And Copilot for Microsoft 365 is helping increase knowledge turns, thus having a cascading effect changing work, work artifacts and workflows and driving better decision-making, collaboration and efficiency.
Microsoft launched one of the ‘Copilot’ type products in 2023, Github Copilot. It’s since added other copilots that augment people and help them be more productive. Copilots are used in a number of cases.
We’re accelerating our innovation, adding over 150 Copilot capabilities since the start of the year. With Copilot and Dynamics 365, we are helping businesses transform every role in business function as we take share with our AI-powered apps across all categories. This quarter, we made our Copilot for Service and Copilot for Sales broadly available, helping customer service agents and sellers at companies like Land O’Lakes, Northern Trust, Rockwell Automation and Toyota Group generate role-specific insights and recommendations from across Dynamics 365 and Microsoft 365, as well as third-party platforms like Salesforce, ServiceNow, and Zendesk.
Copilots for customer service and sales, for enterprise clients, not just for IT and development.
And with our Copilot for Finance, we are drawing context from dynamics, as well as ERP systems like SAP to reduce labor-intensive processes like collections and contract and invoice capture for companies like Dentsu and IDC. ISVs are also building their own co-pilot integrations. For example, new integrations between Adobe Experience Cloud and Copilot will help marketeers access campaign insights in the flow of their work.
Copilots for finance and accounting.
Microsoft is offering copilot services to the major categories that a company like Robert Half services.
Judging the labor market impact of these rollouts in particular, and Gen AI generally, will be beyond my ability. But, I won’t let that stop me.
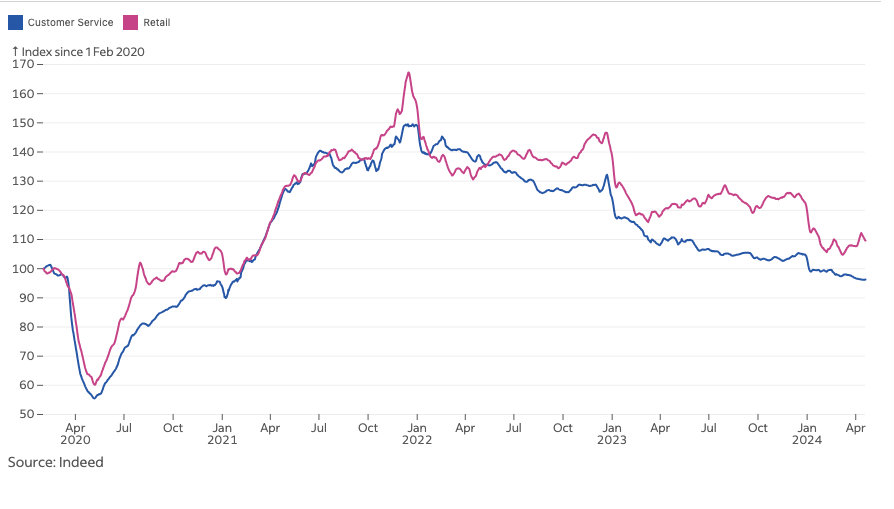
The impact of Gen AI is larger on ‘remote’, less human interactions. Turning to Indeed data and eye balling a potentially relevant comparison — Retail and Customer Service.
Looking at the normalized chart of job postings in the US for customer service and retail, both job categories are down. Both moved in relative synch until about Q4 2022 (when ChatGPT launched). 2023 and 2024 shows a larger deviation between the two job types. This is not close to definitive evidence, but is still a trend worth monitoring.
Looking at the US Labor Market
In Robert Half’s earning call, Andrew Steinerman of JP Morgan asked, is there would be a return to more normal staffing earnings or a ‘spring-loaded rebound’.
Keith Waddel, Robert Half’s CEO responded with this:
I would argue the latter, the spring-loaded rebound. And I’d base that in part on, if you look at the number of job openings, which in the U.S. are just under 9 million. While I understand that's less than their peak where it was in the 12-ish million range, if you compare to prior staffing industry downturns, that 8.9 million is significantly higher than it was at those times. And we view those openings as pent-up demand for future hires, be it contract or perm placement.
To get a sense of this, we can look at the rate of job openings and the unemployment rate from May 2020 to Mar 2024, and then comparing to Dec '2007 to June 2009.
‘Job openings rate’ is unfilled jobs over the labor force. The number of unfilled jobs has dropped from 12.2M at its peak to 8.5M, but the unemployment rate (x-axis) has barely changed. During the Great Recession, moving from 3% to 2% job openings rate corresponded with unemployment rate getting significantly worse.
Staffing Earnings and Gen AI going forward
For staffing firms like Robert Half and Manpower, demand for labor will need to re-accelerate. Currently, to the point of Robert Half’s CEO, there is not a lot of slack in the labor market. Job opening vacancies are still relatively high and unemployment rate is fairly low. That could augur for a bounce back.
It just happens to coincide the launch of Generative AI capabilities in some of its key categories: Accounting, IT, and customer service.